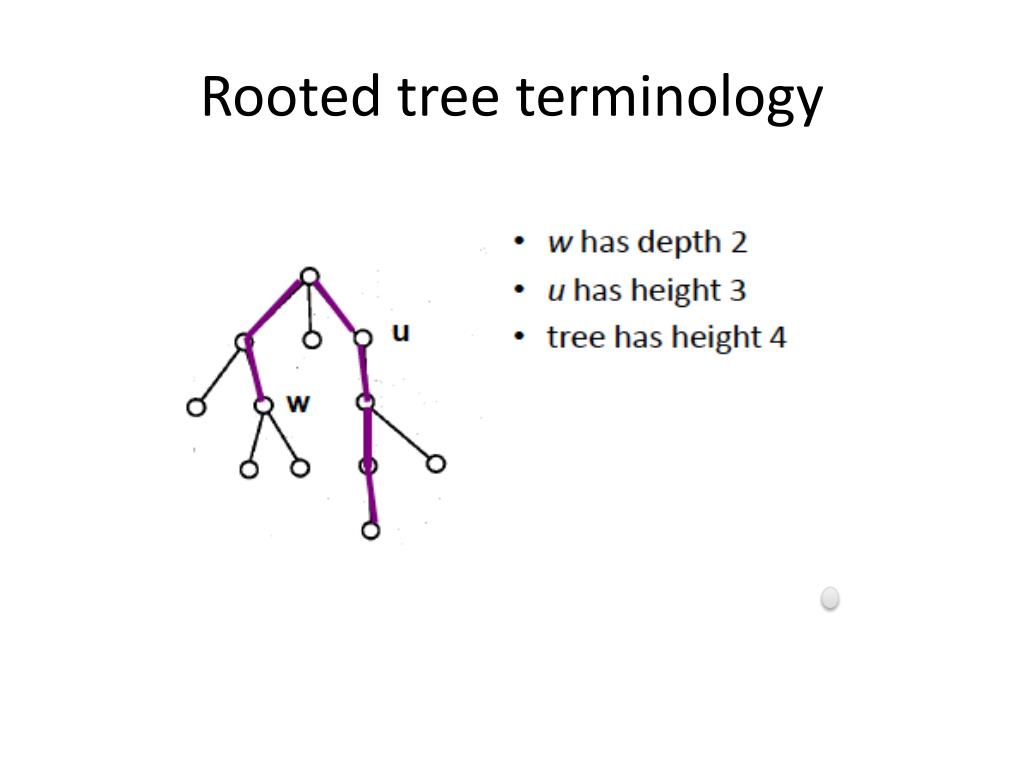
Painstaking Lessons Of Tips About What Is Root Modality

Unraveling the Mystery
1. The Foundation of How We Interact with the World
Ever wondered how you just know something is true, or how you can confidently say something must be the case? That feeling, that underlying sense of certainty or obligation, often comes down to something linguists and philosophers call "root modality." It's not some obscure, dusty academic concept; it's actually woven into the fabric of our everyday language and shapes how we understand possibilities, necessities, and permissions. Think of it like the hidden framework that supports many of our statements about what's possible, what's required, and what's allowed. Without it, we'd have a much harder time navigating social norms and making informed decisions.
Imagine trying to give someone instructions without using words like "must," "can," or "should." It'd be a linguistic tightrope walk! Root modality gives us the tools to express these crucial nuances. It helps us distinguish between "You can borrow my car (if you ask nicely, maybe)" and "You must return it with a full tank of gas!" See the difference? The first expresses a possibility or permission, while the second lays down a non-negotiable requirement. This inherent ability to differentiate is fundamental to our daily interactions.
At its core, root modality deals with our perceptions and expressions of obligation, permission, and ability. It's about the real-world constraints and possibilities that govern our actions and interactions. Its not just about what might be true, but about what is possible given the existing circumstances. Its the "street smarts" of language, helping us understand whats feasible and whats not within a particular context. Without understanding root modality, we risk misinterpreting intentions and potentially creating some awkward (or even disastrous!) social situations.
Think about parenting, for example. A parent might say, "You can play outside after you finish your homework," or "You must clean your room before dinner." These statements aren't just requests; they're declarations of possibility and obligation. They establish the rules of the household, shape a child's behavior, and help the child understand the consequences of their actions. In short, root modality is a critical component of how we communicate expectations and maintain order in all aspects of life.

(PDF) On Root Modality And Thematic Relations In Tagalog English
Digging Deeper
2. Unpacking the Different Flavors of Possibility, Obligation, and Ability
Root modality isn't a monolithic concept; it manifests in different flavors, each expressing a unique type of constraint or possibility. The three primary categories are deontic, dynamic, and epistemic, although only deontic and dynamic are typically considered root modalities.
Deontic modality deals with permission, obligation, and prohibition. It's all about the rules, regulations, and social norms that dictate what we're allowed, required, or forbidden to do. A sign that says "No Smoking" is a clear example of deontic modality in action, explicitly prohibiting a specific behavior. Similarly, a teacher saying, "You may leave the classroom now," grants permission. Deontic modality is essential for maintaining social order and ensuring that everyone knows the boundaries.
Dynamic modality focuses on ability and capacity. It describes what someone or something is capable of doing, based on their inherent qualities or skills. "She can speak five languages" expresses her ability to communicate in multiple languages. "This car can reach 200 mph" describes its performance capacity. Dynamic modality is rooted in the characteristics of the subject itself, independent of external rules or permissions.Although epistemic modality is sometimes considered a type of modality, it is not a root modality. It concerns knowledge and certainty. It expresses the speakers degree of confidence in the truth of a proposition. Statements like "It must be raining" (inferring based on clues) or "It might snow tomorrow" (expressing uncertainty) fall into this category. Epistemic modality is more about our beliefs and deductions than about external permissions or internal abilities.
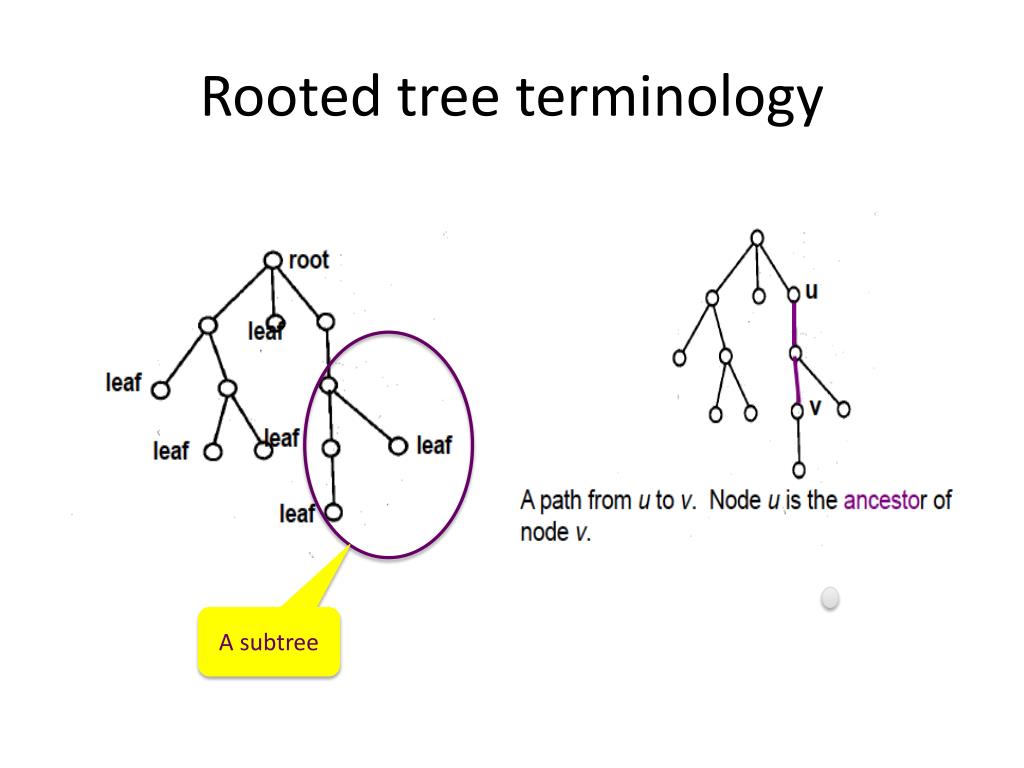
PPT 22C19 Discrete Structures Trees PowerPoint Presentation, Free
Why Does Root Modality Matter?
3. The Practical Implications for Communication and Understanding
So, why should you care about root modality? Because understanding it helps you become a better communicator and a more discerning listener. It allows you to interpret the subtle nuances of language and avoid misunderstandings. It sharpens our abilities to understand complex topics.
Consider this: if someone says, "You should apply for that job," are they giving you friendly advice or a veiled order? The answer depends on the context and the relationship between the speaker and the listener. Recognizing the type of modality being used — in this case, likely deontic, suggesting a degree of obligation — can help you understand the speaker's intention.
In legal and business contexts, understanding root modality is crucial. Contracts often rely on precise language to define obligations and permissions. A poorly worded clause using "may" instead of "must" could have significant legal consequences. Similarly, in negotiations, understanding the other party's expressions of possibility and necessity can help you craft a more successful strategy.
Furthermore, being aware of root modality can enhance your critical thinking skills. It encourages you to question the assumptions underlying statements and to evaluate the evidence supporting claims. It helps you differentiate between genuine possibilities and mere wishful thinking. It is the foundation to truly understand communication nuances.

Lecture 5 Modality Ling 442 Exercises Part 1
Root Modality in Action
4. From Everyday Conversations to Legal Documents
Lets bring this down to earth with some concrete examples. Imagine you're at a restaurant, and the waiter says, "You can order anything on the menu." This is an example of deontic modality granting you permission. It means the restaurant allows you to choose from the available options.
Now, picture a sign in a laboratory that reads, "Safety goggles must be worn at all times." This is another instance of deontic modality, but this time it expresses an obligation. It's a requirement designed to protect your safety, and there are likely consequences for violating it.
Consider a child telling their parent, "I can ride my bike without training wheels!" This is a statement of dynamic modality, asserting their ability to perform a specific action. It's based on their learned skills and physical capabilities.
Even seemingly simple phrases like, "It might rain later," contain modality, albeit epistemic in this case. This expresses a degree of uncertainty based on available evidence (perhaps a cloudy sky or a weather forecast). By recognizing the different types of modality at play, you can gain a more complete understanding of the message being conveyed.

FAQ
5. Your Burning Questions Answered
Still a little fuzzy on the details? Lets tackle some common questions.
6. What's the difference between root and epistemic modality?
Root modality deals with real-world possibilities, obligations, and abilities. Epistemic modality, on the other hand, deals with our beliefs and deductions about the world. Root modality is about what is possible or required; epistemic modality is about what we think is likely or certain.
7. How can I improve my understanding of root modality?
Pay attention to the modal verbs (can, could, may, might, must, should, will, would) used in everyday conversations and written texts. Consider the context in which they're used and ask yourself whether they express permission, obligation, ability, or something else. The more you practice, the better you'll become at recognizing the subtle nuances of modality.
8. Is root modality only important for linguists and philosophers?
Absolutely not! While linguists and philosophers study modality in depth, it's a valuable concept for anyone who wants to improve their communication skills, critical thinking abilities, and overall understanding of the world around them. From navigating social interactions to interpreting legal documents, understanding root modality can give you a significant edge.
9. Where can I learn more about this topic?
Search for linguistics resources online or look for introductory books on semantics or pragmatics. Many online courses and university websites offer materials on modality. Just be prepared for some slightly technical jargon, but don't let that scare you off! The underlying concepts are quite intuitive once you grasp the basics.