Beautiful Tips About How To Know If It Is 3-phase Or Single-phase

How To Tell Single From Three Phase Guide Many Phases Is My House?
Decoding the Mystery
1. Understanding the Basics of Electrical Systems
Ever stared at an electrical panel and felt like you were staring into the abyss? Don't worry, you're not alone. One of the most common questions people have about electricity is how to tell the difference between a 3-phase and a single-phase system. While it might sound intimidating, grasping the basics isn't as hard as you might think. Think of it like understanding the difference between a bicycle (single-phase) and a car (3-phase). Both get you moving, but in very different ways!
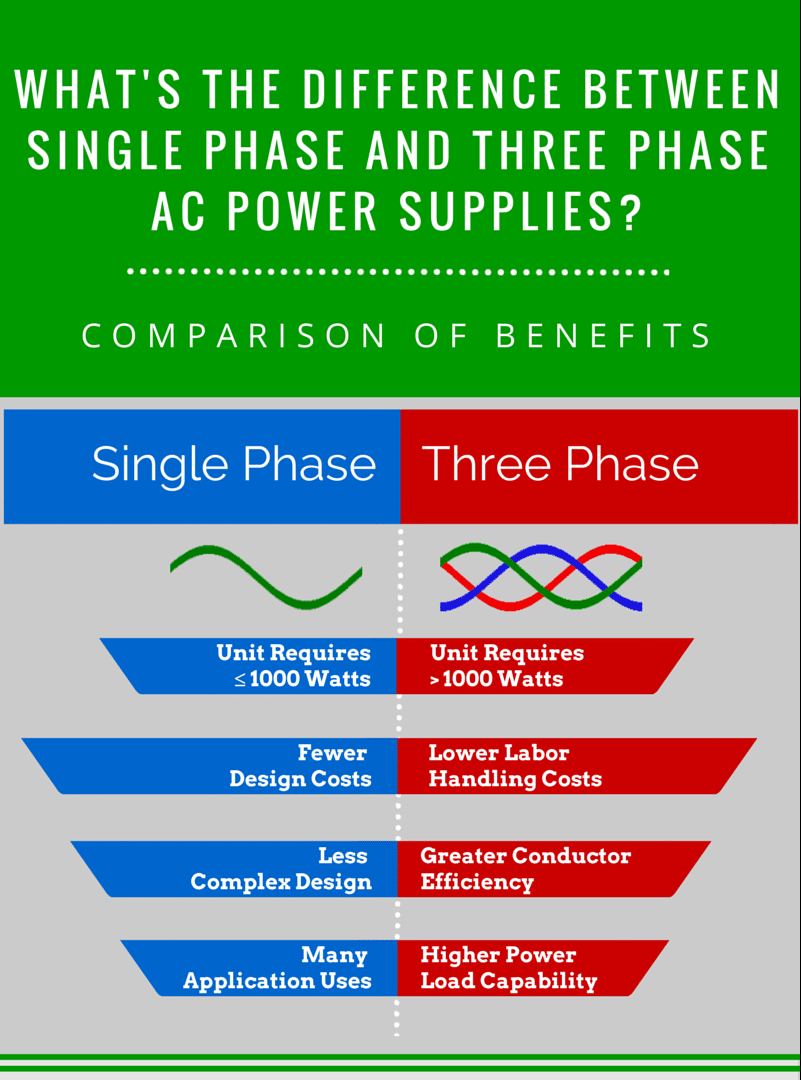
The "phase" in this context refers to the distribution of electrical power. Single-phase is simpler, often found in homes, and generally provides enough power for everyday appliances. Three-phase, on the other hand, is a powerhouse, ideal for industrial settings, large machinery, and anywhere requiring significant electrical muscle. Think of heavy-duty equipment that needs a lot of oomph to operate.
Imagine you're baking a cake. A single-phase system is like using a hand mixer — it's perfectly capable for most recipes. But if you're running a commercial bakery with massive ovens and industrial-sized mixers, you'll need the robust power of a 3-phase system, equivalent to a super-powered, commercial-grade mixer that never quits.
So, how do you actually tell the difference? Well, that's what we're diving into next! We'll explore some practical clues that can help you identify what kind of electrical system you're dealing with. Get ready to Sherlock Holmes your way through electrical circuits!

Spotting the Clues
2. Looking for Telltale Signs
Okay, let's put on our detective hats. One of the easiest ways to distinguish between 3-phase and single-phase is a simple visual inspection. Start by checking the electrical panel itself. Open it up (carefully, and only if you're comfortable doing so — electricity is not something to mess with!). Look at the number of wires coming into the main breaker. Single-phase usually has two "hot" wires and a neutral wire, while 3-phase systems will have three "hot" wires plus a neutral.
Another clue lies in the breaker configuration. Single-phase breakers typically appear in pairs, while 3-phase breakers are often grouped in threes. Imagine a neatly organized row of light switches. In a single-phase setup, you might see switches paired together to control different circuits. In a 3-phase system, you'll likely see groups of three switches controlling more powerful equipment.
Pay attention to the equipment itself. Large appliances like central air conditioners, water heaters, and especially industrial machinery, often require 3-phase power. Check the nameplate on the equipment — it should specify the voltage and phase requirements. If it says something like "208V 3-Phase" or "480V 3-Phase," then you know what you're dealing with. Consider it like reading the label on a can of soup — it tells you what's inside (or, in this case, what kind of power the equipment needs!).
If you see large conduit pipes (the metal or plastic tubes that protect electrical wires) leading to equipment, that can be a hint. Three-phase systems often require larger conduits to handle the increased current. Think of it like a larger pipe needed to carry more water to a powerful sprinkler system. Larger pipes usually indicate a more robust power system.
ThreePhase Installation Design A Comprehensive Guide
Voltage Variations
3. Understanding Voltage Differences
Voltage is essentially the "pressure" that pushes electricity through a circuit. Single-phase systems in homes typically operate at 120V for smaller appliances and 240V for larger ones like dryers and ovens. Three-phase systems, on the other hand, often operate at higher voltages, such as 208V, 480V, or even higher, depending on the industrial application.
Using a multimeter, a handy tool for measuring electrical values, you can carefully check the voltage between the different wires. If you're comfortable and competent using a multimeter, measure the voltage between the phases and between each phase and neutral. If you are not familiar with the use of a multimeter, always consult an electrician to avoid harm or shock.
It's important to note that identifying voltage alone isn't always conclusive. Some single-phase systems can operate at 240V, so it's crucial to combine voltage readings with other visual clues, such as the number of wires and breaker configuration. Think of it like trying to identify a bird by its size alone — you need to consider its color, beak shape, and call to make a definitive identification.
Keep in mind, always exercise extreme caution when working with electricity. If you're unsure about anything, it's best to call a qualified electrician. They have the knowledge, tools, and experience to safely diagnose and work with electrical systems. Safety first, always!

Difference Between Single Phase Meter And Three WAPDA
Application Areas
4. Common Uses and Environments
The applications of single-phase and 3-phase power systems differ significantly. Single-phase is the workhorse for residential buildings. It powers your lights, TVs, refrigerators, and other everyday appliances. Think of it as the reliable energy source for your home's essential needs.
Three-phase power reigns supreme in industrial and commercial environments. It's used to power large motors, heavy machinery, HVAC systems in large buildings, and other high-power applications. Factories, hospitals, and skyscrapers all rely on the robust capabilities of 3-phase power.
Consider a shopping mall. While individual stores might use single-phase power for their lighting and cash registers, the mall's central air conditioning system, elevators, and escalators likely run on 3-phase power. It's all about matching the power requirements to the specific needs of the application.
In agricultural settings, you'll often find 3-phase power used to run irrigation pumps, grain dryers, and other heavy-duty equipment necessary for farming operations. It's the energy backbone that supports modern agriculture and keeps food production running smoothly.

Single Phase Vs. Three How Are They Different? PSC
When in Doubt, Call a Pro
5. Knowing When to Seek Expert Assistance
While understanding the basics of 3-phase and single-phase electrical systems can be helpful, it's crucial to recognize when a task is best left to the professionals. Electricity can be dangerous, and improper wiring or modifications can lead to serious injury, fire, or equipment damage. If you have any doubts or concerns, don't hesitate to call a qualified electrician.
Attempting to diagnose or repair electrical problems without the proper knowledge and tools can be risky. Electricians are trained to identify potential hazards, work safely with electricity, and ensure that all work meets applicable electrical codes. Think of them as the doctors of electrical systems — they have the expertise to diagnose and treat electrical ailments.
Even if you're a seasoned DIY enthusiast, it's wise to consult an electrician for any major electrical work, such as installing new circuits, upgrading your electrical panel, or working with 3-phase systems. Their expertise can save you time, money, and potential headaches down the road. It's always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to electricity.
Remember, your safety and the safety of your property are paramount. Engaging a qualified electrician is an investment in your peace of mind and the long-term reliability of your electrical system. Don't take unnecessary risks — leave the complex electrical work to the experts.

FAQ
6. Frequently Asked Questions About Electrical Phases
Let's tackle some common questions that often pop up about 3-phase and single-phase power:
Q: Can I convert single-phase to 3-phase?
A: Yes, it is possible, but it usually involves specialized equipment like a rotary phase converter or a variable frequency drive (VFD). These devices can be expensive and may not be suitable for all applications. It's best to consult an electrician to determine the best solution for your specific needs. You can think of it as translating from one language to another — it requires specialized tools and knowledge.
Q: What are the advantages of 3-phase power over single-phase?
A: Three-phase power offers several advantages, including higher power capacity, more efficient motor operation, and reduced voltage fluctuations. It's better suited for powering heavy-duty equipment and industrial applications where consistent and reliable power is essential. Think of it as the difference between a regular highway and a superhighway — 3-phase can handle a much larger volume of traffic (electricity) more efficiently.
Q: How do I know if my business needs 3-phase power?
A: If your business uses large motors, industrial machinery, or other high-power equipment, you likely need 3-phase power. Also, your local utility company can advise you on the best electrical service for your specific needs. Before leasing or purchasing a commercial property, confirm with the property owner or utility company the availability of the electrical service.