Amazing Tips About How To Know If It's AC Or DC
Unraveling the Mystery
1. Spotting the Current Type
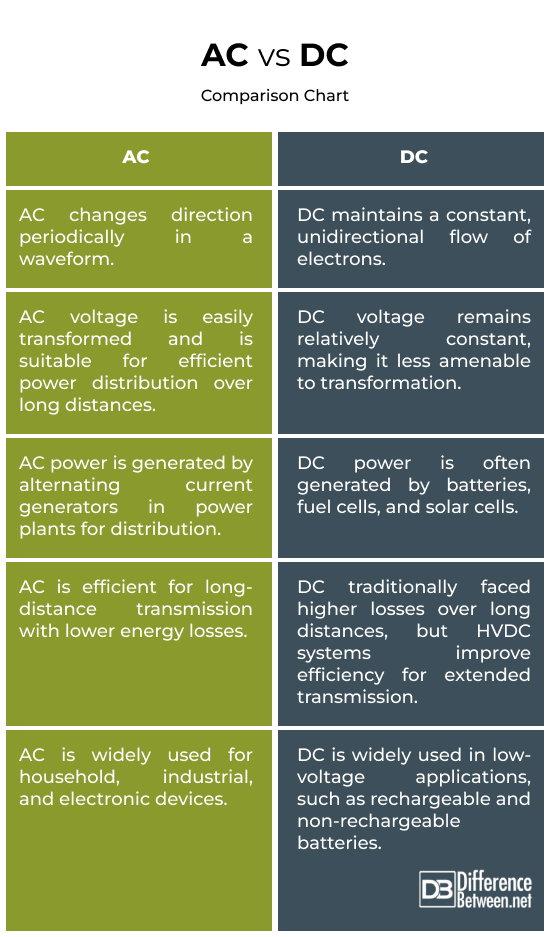
Ever wondered what powers your appliances? Is it AC or DC? Its a common question, and getting it right can be surprisingly important, especially when dealing with electronics. Think of AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) as different types of energy delivery systems, each with its own unique characteristics and best-use scenarios. It's like choosing between a sprinter and a marathon runner — both run, but they do it very differently!
So, how do you know which one you're dealing with? Well, let's start with the basics. AC is like a wave, constantly changing direction. This makes it super efficient for transmitting power over long distances, which is why its used in most household outlets. DC, on the other hand, flows in one direction, like a river. It's generally preferred for electronic devices because it provides a stable and consistent power supply. Ever wondered why your phone charger has that bulky adapter? It's converting AC from the wall into DC for your phone's delicate circuits.
One of the easiest ways to tell the difference is to look at the power source itself. Wall outlets in most homes deliver AC. Batteries, on the other hand, always provide DC. If you're dealing with an appliance that plugs directly into the wall, it's almost certainly running on AC. If it uses batteries or a power adapter, chances are its using DC. It's a pretty straightforward clue, but always double-check!
Another helpful hint lies in the device's purpose. Devices that require precise and steady power, like computers and smartphones, typically operate on DC. Larger appliances that need to handle high voltage and current, such as refrigerators and ovens, usually use AC. It's all about the best match for the job at hand — and keeping everything running smoothly (and safely!).
Identifying AC and DC Sources
2. Examining Plugs, Adapters, and Batteries
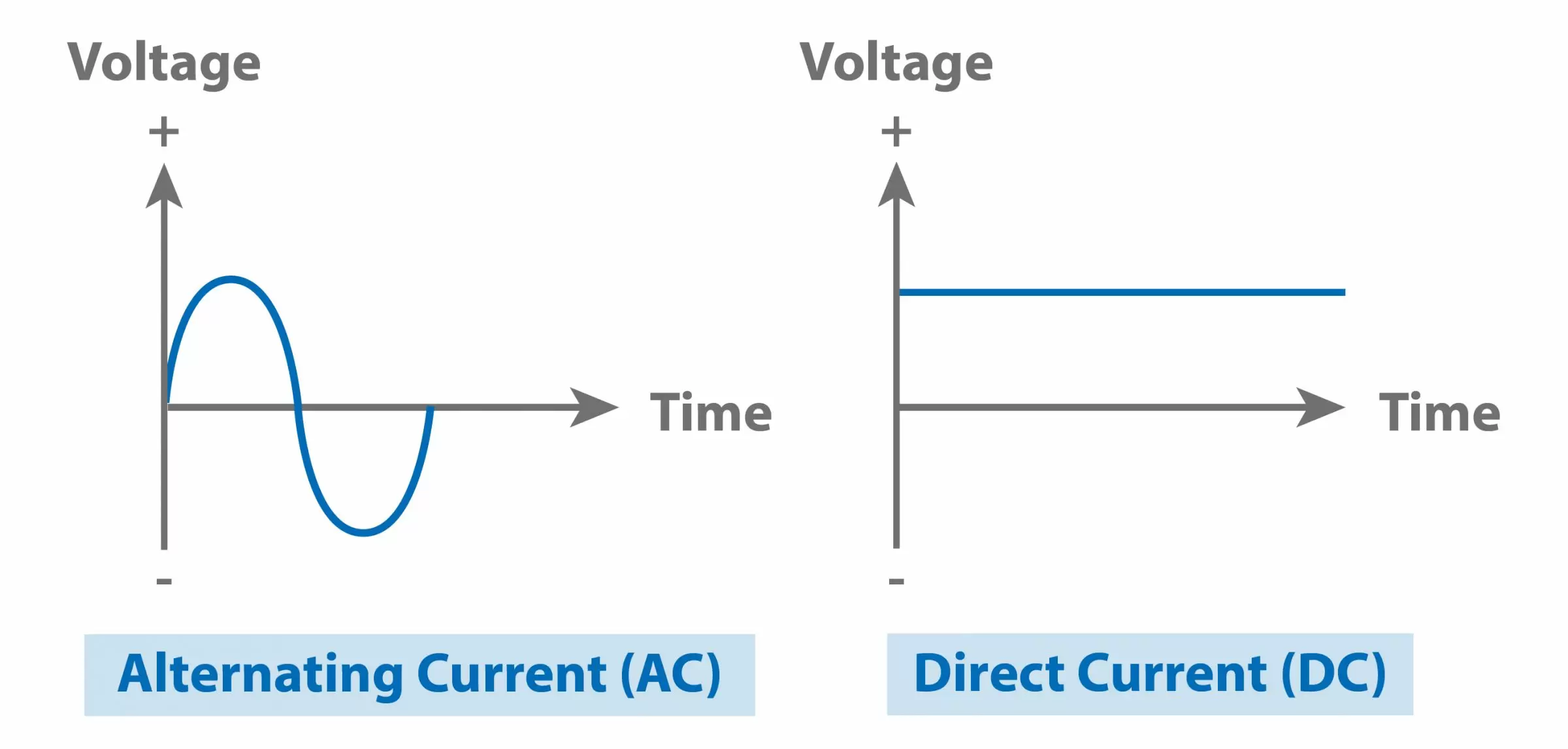
Lets dive a little deeper into how to spot the difference between AC and DC sources. One of the simplest methods is to check the power adapter or charger. Most adapters will clearly label the output voltage and the type of current it delivers. Youll typically see something like "Output: 5V DC" or "Output: 12V AC." This is a dead giveaway and saves you from having to guess!
When it comes to plugs, you generally won't see a label directly on them stating AC or DC. However, the fact that it plugs into a standard wall outlet is a strong indicator that it utilizes AC power. Keep in mind though that just because something has a standard plug, it doesn't always mean it runs directly on AC. Many devices, as we've mentioned, use adapters to convert AC power to DC before it reaches the device itself.
Batteries, on the other hand, are almost always DC power sources. You'll find that batteries are essential for devices that need to be portable or operate independently of a wall outlet. Whether it's a tiny watch battery or a large car battery, they all provide a steady stream of DC power. Look for the "+" and "-" symbols on the battery to indicate the positive and negative terminals, which are characteristic of DC circuits.
Understanding these visual cues is crucial, but always remember safety first! Never tamper with electrical components unless you are qualified to do so. When in doubt, consult a professional or refer to the device's manual. After all, playing it safe is always the best strategy when dealing with electricity.

Using a Multimeter
3. Measuring Voltage and Current
For those who like a more technical approach, a multimeter is your best friend. This handy tool allows you to directly measure the voltage and current of a circuit, helping you definitively determine whether it's AC or DC. Don't worry, it's not as intimidating as it sounds! You'll just need to follow a few simple steps.
First, set your multimeter to the appropriate mode: AC voltage (V~) for measuring alternating current, or DC voltage (V-) for measuring direct current. If you're unsure which one to use, start with AC voltage. Connect the multimeter probes to the circuit you want to test. The red probe goes to the positive side (if there is one), and the black probe goes to the negative or ground side.
Once connected, the multimeter will display a reading. If the reading is stable and consistent, it's likely DC voltage. If the reading fluctuates or shows a sine wave pattern, it's most likely AC voltage. The numerical value will tell you the voltage level, which can be useful for troubleshooting and ensuring the circuit is operating within its intended range.
Using a multimeter can be a valuable skill for anyone interested in electronics or electrical work. It provides precise measurements and eliminates guesswork. Just remember to always exercise caution and follow safety guidelines when working with electrical circuits. It's better to be safe than sorry!

Why Does it Matter? AC vs. DC in Different Devices
4. The Implications for Electronics and Appliances
So, why all the fuss about AC and DC? Well, using the wrong type of current can have serious consequences for your devices. Electronic components are typically designed to operate on a specific type of current, and using the wrong one can cause damage, overheating, or even complete failure. Imagine trying to fuel a diesel engine with gasoline — not a pretty picture!
For example, most modern electronics, like laptops, smartphones, and tablets, rely on DC power. This is because these devices use sensitive electronic components that require a stable and consistent power supply. Supplying AC directly to these devices would likely fry their delicate circuits. That's why you see those adapters converting AC from the wall into the DC needed by the device.
On the other hand, larger appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners often operate on AC power. These appliances require higher voltage and current to function efficiently, and AC is better suited for transmitting power over long distances. Trying to run these devices on DC would be inefficient and impractical.
In summary, understanding the difference between AC and DC is crucial for ensuring the proper operation and longevity of your devices. It's not just a matter of knowing what type of current they use, but also understanding why they use it. This knowledge can help you troubleshoot problems, prevent damage, and make informed decisions about your electrical equipment.

Explain Difference Between Ac And Dc
AC/DC Safety Tips and Best Practices
5. Protecting Yourself and Your Devices
Working with electricity, whether AC or DC, always requires caution and respect. While AC can be more dangerous due to its higher voltage levels, both types of current can pose risks if not handled properly. Follow these safety tips to protect yourself and your devices.
First and foremost, never tamper with electrical wiring or components unless you are qualified to do so. Electricity is invisible and can be deadly. If you're not comfortable working with electricity, always consult a professional electrician. It's better to pay a little extra for expert help than to risk your safety or damage your equipment.
When using adapters or chargers, always make sure they are compatible with your devices and the voltage of your electrical outlet. Using the wrong adapter can damage your device or even cause a fire. Check the specifications on the adapter and the device to ensure they match. Overloading circuits is also a big no-no. Avoid plugging too many devices into a single outlet, as this can cause the circuit breaker to trip or even start a fire.
Finally, be mindful of water and electricity. Never use electrical devices near water, as water can conduct electricity and create a dangerous shock hazard. If an electrical device gets wet, unplug it immediately and allow it to dry completely before using it again. By following these safety tips, you can minimize the risks associated with AC and DC power and ensure the safety of yourself and your family.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your AC/DC Questions Answered
Still scratching your head about AC and DC? Here are some common questions (and their answers!) to help clear things up:
7. Question 1
Answer: Absolutely! That's precisely what adapters and inverters do. Adapters convert AC from your wall outlet to DC for devices like phones and laptops. Inverters do the opposite, converting DC power from batteries (like in a car) to AC for running appliances. It's all about matching the power source to the device's needs.
8. Question 2
Answer: While both AC and DC can be dangerous, AC is generally considered more hazardous at higher voltages. AC's alternating nature can interfere with the heart's electrical signals, making it more likely to cause ventricular fibrillation. That being said, both types of current should always be treated with respect and caution.
9. Question 3
Answer: That's an interesting question! While AC remains the dominant force for long-distance power transmission, DC is making a comeback in certain areas. High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission is becoming more common for transmitting power over very long distances, and DC is also gaining traction in renewable energy systems and energy storage. The future might see a more balanced mix of both AC and DC, depending on the specific application.