Glory Tips About Is The Sun AC Or DC

Getting The Best Out Of AC Vs DC Power RayPCB
Unveiling the Sun's Electrical Nature
1. Journey to the Core of Solar Power
Alright, let's tackle a question that might just make you squint at the sun a little differently: Is the sun AC or DC? Now, before you start picturing tiny little solar panels sprinkled across the sun's surface (which, let's be honest, is a pretty funny image), let's clarify what we're actually asking. We're not talking about the kind of electricity powering your phone. Instead, we are diving into the realm of how energy is generated within the sun itself and how it interacts with its environment.
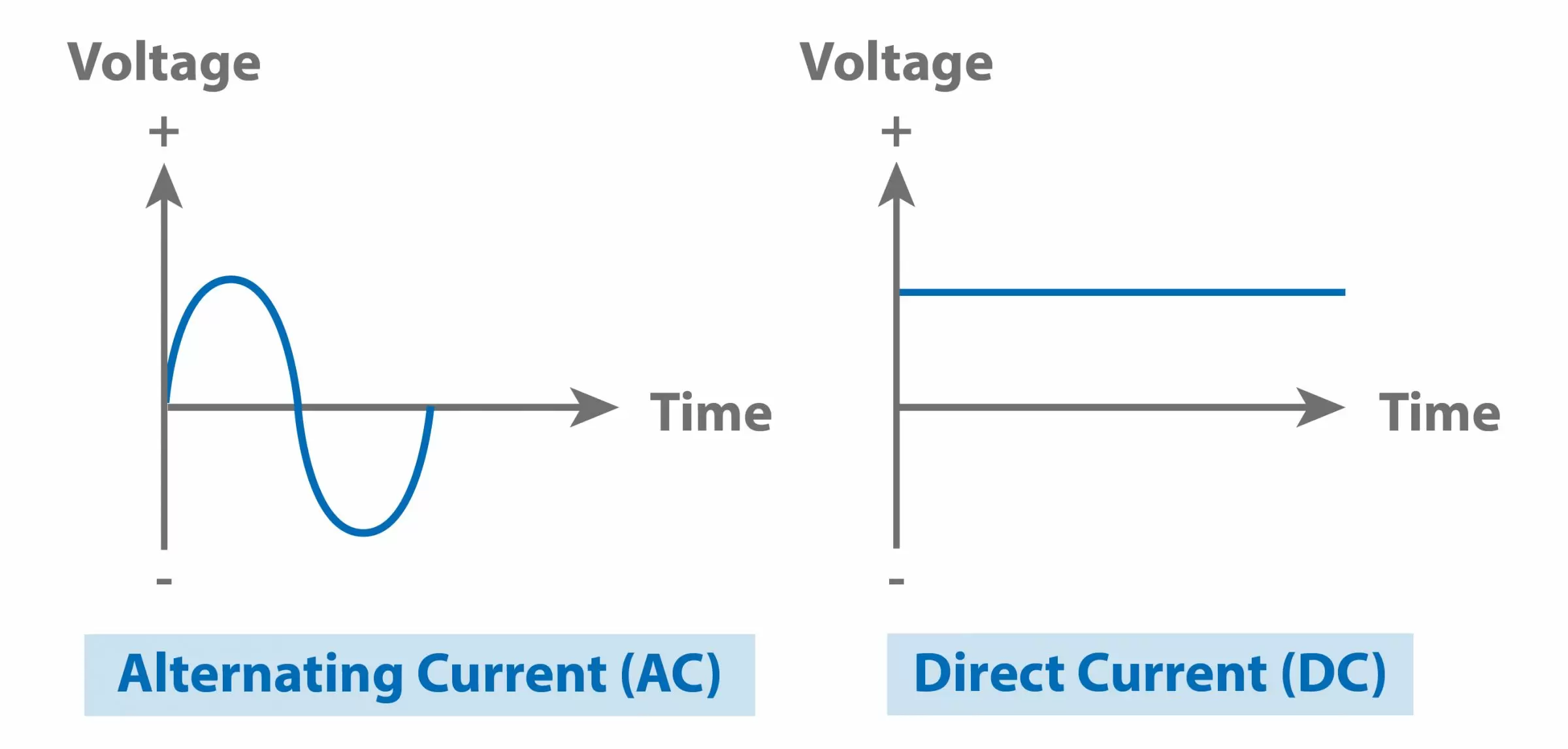
To understand the sun's "electrical personality," we need to understand the basic difference between Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). Think of it like this: DC is like a one-way street for electrons; they flow in a single direction. AC, on the other hand, is like a two-way street with electrons constantly changing direction. It's this directional shift that distinguishes AC from DC, and it's crucial to how we power our homes using the power grid.
The Sun, in essence, is a gigantic nuclear reactor. Deep inside its core, hydrogen atoms are smashed together under immense pressure and heat, creating helium and releasing a massive amount of energy. This energy isn't directly electrical in the way we might initially think, but it sets the stage for some pretty interesting electromagnetic phenomena. The sun's activity affects Earth via solar winds.
Understanding the sun's behavior is so important because it directly impacts our planet. From the beautiful aurora borealis (Northern Lights) to potential disruptions in communication systems, solar activity plays a significant role in our daily lives. So, let's explore deeper into the world of magnetic fields, plasma, and the amazing dance of energy happening within our nearest star.
The Sun's Inner Workings
2. Decoding the Solar Symphony
At its heart, the sun is a seething ball of plasma. Plasma is often referred to as the fourth state of matter (after solid, liquid, and gas), where atoms are so energized that they lose their electrons, resulting in a soup of ions and free electrons. The Sun's core is unbelievably hot. Temperatures exceed 15 million degrees Celsius. These charged particles, zipping around at incredible speeds, are what give the sun its electromagnetic properties.
The movement of these charged particles generates incredibly powerful magnetic fields. These magnetic fields aren't static; they're constantly twisting, tangling, and reconfiguring themselves. Think of it like a colossal, ever-changing magnetic sculpture, sculpted by the flow of plasma. The Sun's magnetic field is complex, and it impacts many things.
These magnetic field lines sometimes become so stressed that they snap and reconnect, releasing enormous bursts of energy in the form of solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). These events can send huge amounts of charged particles hurtling out into space, some of which eventually reach Earth. These solar activities are always being monitored by scientists.
Now, to bring it back to our initial question: does this chaotic electromagnetic activity resemble AC or DC? Well, it's not a straightforward answer. While there isn't a simple "switch" that flips the current back and forth like in an AC circuit, the constant shifting and reconnection of magnetic fields create a highly dynamic and variable electromagnetic environment. It's more like a super-charged, ever-changing mix of both, leaning towards a chaotic DC that is not really DC.

Solar Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections
3. Understanding the Solar Eruptions
Let's talk about the Sun's occasional tantrums: solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). Solar flares are sudden releases of energy from the Sun's surface, emitting intense radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum — from radio waves to X-rays and gamma rays. They are usually associated with active regions around sunspots, where magnetic fields are particularly strong and complex.
CMEs, on the other hand, are huge expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun's corona (the outermost layer of its atmosphere). These ejections can contain billions of tons of matter and travel at speeds of up to several million miles per hour. When a CME hits Earth, it can cause geomagnetic storms, which can disrupt radio communications, damage satellites, and even cause power outages. Solar storms have impacted technology.
The intensity and frequency of these solar events vary over an approximately 11-year cycle, known as the solar cycle. During solar maximum, the Sun is more active, with more sunspots, flares, and CMEs. During solar minimum, the Sun is quieter, with fewer such events. Scientists keep a close watch on this cycle to anticipate and mitigate the effects of solar activity on Earth.
These events showcase the sun's dynamic nature, but still don't answer the AC/DC question directly. They illustrate the incredible power and complexity of the sun's electromagnetic activity, which is driven by the plasma and magnetic fields within. They also impact us here on Earth, and is why solar monitoring and research is important.

Dc Generator Vs Ac
Impact on Earth
4. How Solar Weather Affects Us
So, what happens when the sun "sneezes" and sends a CME our way? Well, the Earth's magnetic field acts as a shield, deflecting most of the charged particles. However, some particles can still penetrate the magnetic field near the poles, causing the beautiful aurora borealis (Northern Lights) and aurora australis (Southern Lights). These light displays are a visual manifestation of the interaction between the sun's particles and Earth's atmosphere.
Geomagnetic storms, caused by CMEs, can also disrupt radio communications, particularly high-frequency (HF) radio, which is used by airplanes, ships, and amateur radio operators. The increased ionization in the ionosphere can absorb or scatter radio waves, making it difficult to communicate over long distances. Satellites in orbit are also vulnerable to geomagnetic storms. The charged particles can damage electronic components and degrade the performance of solar panels.
In extreme cases, geomagnetic storms can even cause power outages on Earth. The changing magnetic fields can induce currents in long power lines, overloading transformers and causing them to fail. The most famous example is the 1989 Quebec blackout, which left millions of people without power for several hours. This emphasizes the importance of understanding and predicting solar weather to protect our infrastructure.
Ultimately, while the sun doesn't neatly fit into the AC or DC categories, its constantly fluctuating electromagnetic activity has a very real impact on our planet. From stunning light shows to potential disruptions in technology, the sun's influence is undeniable. It showcases the complex and dynamic interactions within our solar system, and the importance of continued research and monitoring of solar activity. This will help us prepare for the future.

SUN 600W DC To AC Inverter Shop Today. Get It Tomorrow!
The Verdict
5. Beyond Simple Labels
So, after this journey, can we definitively say the Sun is AC or DC? The answer, as you might have guessed, is no. The Sun's electrical nature is far more complex than a simple alternating or direct current. It is a swirling, chaotic mix of charged particles and magnetic fields, constantly changing and interacting. The sun isn't so easy to put in one box.
The term "DC" would be closer, but even that falls short. While the overall flow of energy is generally outward, the Sun's dynamic magnetic fields and plasma create a highly variable and unpredictable electromagnetic environment. Trying to label it as AC or DC is like trying to describe the ocean as simply "wet"; it misses the immense complexity and dynamism of the system.
What we can say is that the Sun is a powerful source of electromagnetic energy that plays a crucial role in our solar system. Understanding its behavior is essential for protecting our technology and infrastructure, and for gaining a deeper understanding of the universe around us. The sun is crucial to life on Earth.
Instead of trying to force the Sun into a neat electrical box, let's appreciate it for what it is: a dynamic, powerful, and essential force in our solar system. Perhaps we need a new term to describe its unique electrical characteristics — something like "Chaotic Electromagnetic Flow," but maybe that needs some workshopping! The Sun is full of many surprises.

FAQ
6. Answering Your Solar Queries
Q: What would happen if the sun suddenly turned off?A: If the sun suddenly went out, Earth would quickly become a frozen wasteland. Photosynthesis would stop, plants would die, and the temperature would plummet. Within a few months, the oceans would begin to freeze over, and within a year, Earth's surface temperature would drop to well below zero. It would be a very bad day (or rather, a very long, dark night).
Q: Can we harness the Sun's energy more efficiently?A: Absolutely! Scientists and engineers are constantly working on improving solar panel technology and developing new ways to harness the Sun's energy. This includes research into more efficient solar cells, better energy storage solutions, and even space-based solar power, which would collect solar energy in space and beam it back to Earth.
Q: Is the sun getting hotter or colder?A: The Sun's energy output does fluctuate slightly over the 11-year solar cycle, but overall, it's been remarkably stable over billions of years. However, as the Sun ages, it is gradually getting brighter and hotter, at a very, very slow rate. This gradual increase in solar luminosity is something that scientists are studying to understand its long-term effects on Earth's climate.