Marvelous Tips About How Fast Is The Speed Of Dark

The Speed Of Dark
Chasing Shadows
Ever pondered something so profoundly philosophical that it makes your brain do a little somersault? Well, get ready for another one! We're diving headfirst into the fascinating, slightly paradoxical, and definitely mind-bending concept of the "speed of dark." But hold on a second, does darkness even have a speed? Isn't it just the absence of light? Prepare to have your perceptions challenged!
1. What Exactly Are We Talking About?
Let's clarify something right off the bat. The "speed of dark" isn't about some mysterious force zipping through the cosmos. Instead, it's a playful way to describe how quickly darkness appears when light disappears. Think of it like this: Imagine you're standing in a brightly lit room, and suddenly the lights go out. The darkness doesn't "travel" to you; it simply is the absence of light that was there a moment before. It's more about the propagation of a change in the luminous environment.
Now, let's inject a bit of physics. When we say "speed of light," we're talking about photons, massless particles that travel at an incredible 299,792,458 meters per second in a vacuum. Darkness, lacking any physical substance, doesn't operate under the same rules. The rate at which darkness seems to "spread" is more accurately the rate at which light is removed or blocked.
So, is there a way to measure it? Not in the conventional sense of measuring something tangible moving through space. The perception of darkness filling a space can be instantaneous, especially in small areas. However, the gradual transition from light to dark can be influenced by factors like atmospheric conditions or the size of the light source being extinguished. This makes the "speed of dark" a relative and perceptual phenomenon rather than a strict physical quantity.
Consider a solar eclipse. As the moon gradually obscures the sun, darkness descends. The speed at which this darkness "moves" across the landscape is related to the moon's movement and the size of its shadow. It's not darkness racing to fill the void, but rather the absence of sunlight spreading across the Earth's surface.

Light's Out
2. The Perceptual Game
The sensation of darkness enveloping us isn't just about physics; it's also heavily influenced by our perception. Our eyes and brains are constantly adjusting to varying levels of light. When the lights go out, our pupils dilate to allow more light in, which is why it takes a few moments for us to see clearly in the dark. During this adjustment period, the "speed of dark" can feel incredibly fast.
Think about how your eyes react when you step from bright sunlight into a dimly lit room. It takes a while to adjust, right? The sudden lack of light creates a strong impression of darkness rushing in, even though it's simply your eyes adapting to the new conditions. This adaptation process varies from person to person. Some people adjust faster than others. How quickly your vision adapts affects your perception of the "speed of dark".
It's important to remember that the brain is a masterful storyteller. It fills in gaps, interprets signals, and creates a coherent experience of the world around us. In the case of darkness, our brain creates the sensation of something "moving in" even though it's simply the cessation of light. It's like watching a magician — you know it's an illusion, but your brain still gets fooled!
Dark adaptation is a key aspect of how we perceive the "speed of dark". The darker the environment, the longer our eyes take to fully adjust. This adaptation process involves changes in the sensitivity of our photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) in the retina. When light is removed, these cells become more sensitive to lower light levels, enhancing our ability to see in the dark. This process influences our perception of how rapidly darkness descends, especially in situations where the transition from light to dark is gradual.

The Speed Of Dark
The Speed of Light's Retreat
3. When Light Goes Away
Rather than thinking of darkness as an entity with its own speed, it's more accurate to view it as the absence of light. So, the "speed of dark" is essentially determined by how quickly light is removed or blocked. If you flick off a light switch, the light disappears almost instantaneously (at the speed of light, of course!), and the darkness fills the void equally fast.
Now, imagine a scenario where light is gradually fading, like during sunset. The "speed of dark" in this case is much slower, as the light intensity decreases gradually over a longer period. This gradual change allows our eyes to adapt more smoothly, resulting in a less dramatic perception of darkness "spreading." The rate at which light diminishes is directly tied to how we experience the transition to darkness.
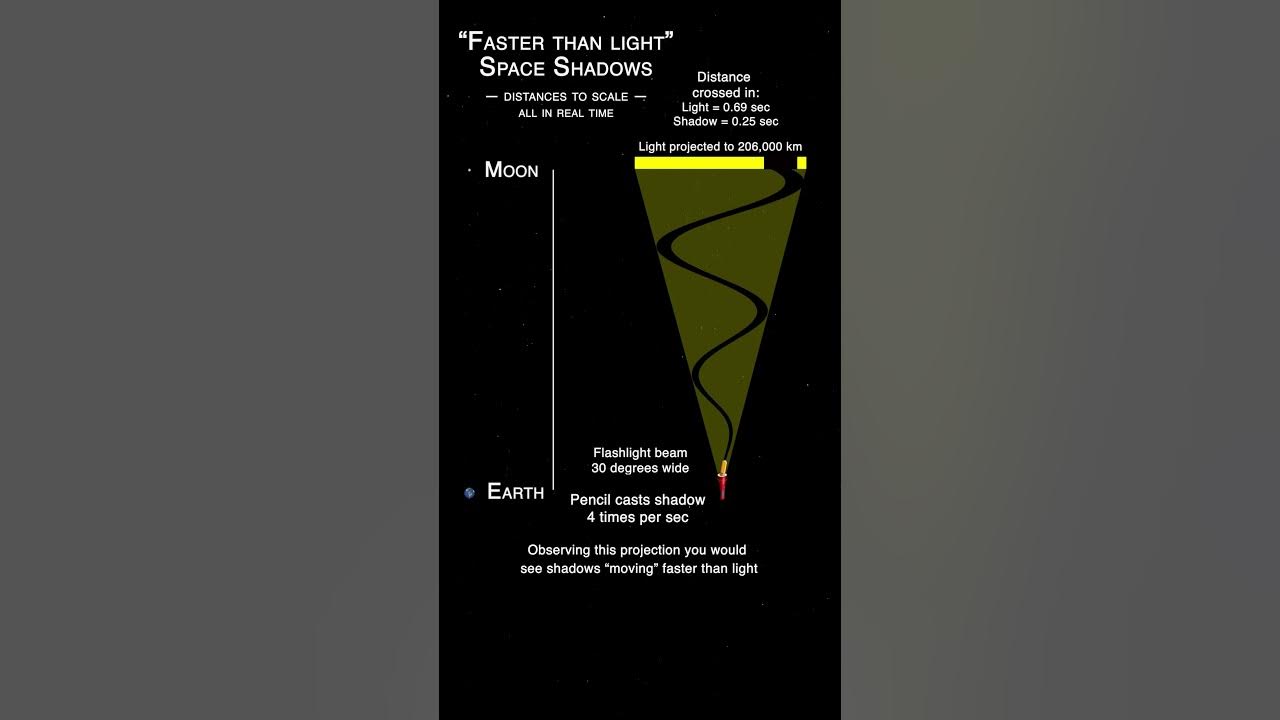
Consider the way a shadow forms. A shadow is simply an area where light is blocked. The shape and size of the shadow depend on the size and shape of the object blocking the light, as well as the position of the light source. The "speed" at which the shadow appears to move depends on the movement of the object or the light source. Again, it's not darkness moving, but the boundary of the light being altered.
Think of it like watching a dimmer switch being turned down. The light doesn't disappear instantly; it fades gradually. This fading process impacts our perception of the transition to darkness. As the light dims, the "speed of dark" seems slower and more gradual than if the light were simply switched off abruptly.
The Speed Of Dark (Faster Than Light) YouTube
Delving Deeper
4. Cosmic Shadows and Light Years
The concept of the "speed of dark" also has fascinating implications in the realm of astronomy. While darkness itself doesn't travel, the blocking of light from distant celestial objects can create spectacular phenomena, such as eclipses and occultations. These events allow astronomers to study the properties of the objects involved and the space between them.
For example, when a star passes behind a planet, the light from the star is blocked, creating a shadow. The speed at which this shadow "moves" across the face of the planet (as observed from Earth) is determined by the relative motion of the star and the planet. By studying the timing and shape of the shadow, astronomers can learn about the planet's atmosphere and its size.
Furthermore, consider the vast distances in space. Light from distant galaxies takes billions of years to reach us. If a star in one of those galaxies were to suddenly explode and disappear, the darkness wouldn't "travel" to us. Rather, the light from that star would simply stop reaching us after billions of years. The perception of that star disappearing would be delayed by the vastness of space.
Astronomers often use the term "light-years" to measure distances in space. A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year. If a star is 100 light-years away, it means that the light we see from that star today left it 100 years ago. In a sense, we're always observing the past when we look at distant objects in the universe. This delay highlights the complex relationship between light, time, and our perception of events in the cosmos.

Putting It All Together
5. Embracing the Paradox
Ultimately, the "speed of dark" is a playful concept that highlights the difference between our perception of reality and the underlying physics. It's a reminder that darkness isn't a substance with its own speed, but rather the absence of light. The rate at which darkness appears depends on how quickly light is removed or blocked, as well as our own visual and cognitive processes.
So, next time you're sitting in a darkened room, contemplating the mysteries of the universe, remember that the "speed of dark" is more about the dance of light and shadow than about any inherent property of darkness itself. It's a chance to appreciate the intricate workings of our senses and the way our brains interpret the world around us.
Think of it as a thought experiment. It's less about finding a definitive scientific answer and more about stimulating curiosity and exploring different perspectives. By questioning seemingly simple concepts, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex and fascinating nature of reality. Besides, pondering the "speed of dark" makes for a pretty good conversation starter at parties!
In a way, the pursuit of understanding the "speed of dark" is a journey into the nature of perception. It pushes us to consider how our senses, our brains, and our experiences shape the way we see the world. It is this inquiry that allows a fuller understanding of light, space, and time.

The Speed Of Dark
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
6. Q
A: No, the "speed of dark" isn't a scientifically defined term. It's a conceptual way to describe how quickly we perceive darkness when light disappears. It's more about perception and the absence of light rather than a physical phenomenon.
7. Q
A: Several factors influence our perception, including the speed at which light is removed or blocked, our eyes' adaptation to darkness, and our brain's interpretation of the change in light levels.
8. Q
A: No, it's misleading to compare the "speed of dark" to the speed of light. The speed of light is a fundamental constant, while the "speed of dark" is a perceptual phenomenon related to the removal of light, not something traveling through space.