Build A Tips About Can I Connect 4 12V Batteries To 24V Inverter
4 Battery 24 Volt Wiring Diagram »
Connecting Batteries to Your 24V Inverter
1. Understanding Voltage and Series Connections
So, you're thinking about hooking up four 12V batteries to your 24V inverter? Smart move! It's a common question, and the answer is generally yes, but with a few crucial considerations. Think of it like baking a cake — you can't just throw all the ingredients together and hope for the best, right? You need to follow the recipe (or in this case, understand the wiring). The key concept here is voltage.
A 24V inverter needs, well, 24 volts! Batteries, like power tools, come in different voltages. To get the voltage you need, you'll likely be connecting those batteries in series. A series connection is when you connect the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the next, and so on. This adds the voltages together. Two 12V batteries in series will give you 24V.
But where do the other two batteries come in? That's where things can get interesting! They can play different roles, depending on your needs and how you connect them. You might use them for increased capacity (meaning longer run time) using a series-parallel configuration, or maybe you have a specific charging setup in mind. The important thing is to understand the impact on voltage and current.
Imagine each battery as a water tank. Voltage is like water pressure, and current is like the flow rate. Connecting batteries in series increases the "pressure" (voltage), while connecting them in parallel increases the "flow rate" (current capacity). You need to match the "pressure" to your inverter's requirements and have enough "flow" to power your devices. Improper configuration could lead to inefficient operation or even damage. Keep reading to understand which connection is right for you!
![[DIAGRAM] A Solar Panel Wiring Diagram 24 Volt To 12 Inverter [DIAGRAM] A Solar Panel Wiring Diagram 24 Volt To 12 Inverter](https://www.mobile-solarpower.com/uploads/1/2/9/6/12964626/111-orig_orig.jpg)
Series vs. Parallel
2. Navigating Wiring Configurations
Let's break down the difference between series and parallel connections. As we discussed, a series connection adds the voltages together. So, if you connect two 12V batteries in series, you get 24V, but the amp-hour (Ah) capacity (which determines how long the batteries will last) remains the same as a single battery. For example, two 12V 100Ah batteries in series gives you 24V and 100Ah.
A parallel connection, on the other hand, keeps the voltage the same but adds the amp-hour capacity. So, connecting two 12V batteries in parallel gives you 12V but doubles the Ah capacity. Two 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel gives you 12V and 200Ah. You will NOT want to hook your batteries up in parallel for your inverter, it will only provide 12V to a 24V system
So, with four 12V batteries and a 24V inverter, the most common approach is to create two sets of batteries connected in series (24V each), then connect these two sets in parallel. This is called a series-parallel configuration. In this scenario, you maintain the 24V needed for the inverter, and double the amp-hour capacity. So four 12V 100Ah batteries in a series-parallel configuration gives you 24V and 200Ah.
Think of it this way: you need the right "pressure" (voltage) to get things started, and enough "flow" (capacity) to keep things running. The series-parallel connection offers a good balance, allowing you to power your 24V inverter for a longer time. However, it's extremely important that all four batteries are the same model, age, and have similar charge levels for a series-parallel connection.

How Many Batteries Do I Need For A 1000W Or 2000W Power Inverter
Safety First
3. Protecting Yourself and Your Equipment
Working with batteries can be a bit like dealing with a grumpy cat — you need to be careful! Batteries store a lot of energy, and if something goes wrong, it can be dangerous. Always wear safety glasses and gloves when working with batteries. Short circuits can cause sparks, heat, and even explosions. Seriously, protect your peepers!
Make sure your batteries are in good condition. Check for any signs of damage, like cracks or leaks. Don't use batteries that are damaged, as they can be unstable and pose a safety hazard. And never mix old and new batteries, or batteries of different types or sizes, especially in a series-parallel configuration. This can cause uneven charging and discharging, which can shorten the lifespan of your batteries and even damage them.
Proper ventilation is also crucial, especially when charging batteries. Charging can release gases, so make sure you're in a well-ventilated area to prevent a buildup of these gases. And always use a charger that's specifically designed for the type of batteries you're using. A mismatched charger can overcharge or undercharge your batteries, which can reduce their lifespan and create safety hazards.
Finally, double and triple-check your wiring before connecting anything to the inverter. A mistake in the wiring can cause a short circuit, which can damage your batteries, your inverter, and even cause a fire. Take your time, follow the diagrams carefully, and if you're not sure about something, consult a professional. Safety first, fun later!

4 Battery 24 Volt Wiring Diagram »
Choosing the Right Inverter for Your Needs
4. Matching Inverter Size to Your Power Demands
So you have a plan for your batteries, but is your inverter up to the task? Inverters come in different sizes, measured in watts. You need to choose an inverter that can handle the power demands of all the devices you plan to run simultaneously. Overloading an inverter can damage it, so it's better to err on the side of caution and choose an inverter that's slightly larger than you think you need. It also depends on what you want to use the batteries for.
Figure out the wattage requirements of your devices. Check the labels on your appliances and electronics to find their wattage ratings. Add up the wattage of all the devices you plan to run at the same time. This will give you an estimate of the total power you need from your inverter. You can even find online calculators that will allow you to make your sums easier.
Consider surge loads. Some devices, like refrigerators and power tools, require a surge of power when they start up. Your inverter needs to be able to handle these surge loads, so make sure it has a surge capacity that's high enough to accommodate them. Typically an inverter will need to be three times larger than the wattage of the device that will be started to handle the surge. Check if your inverter has peak wattage and continuous wattage, and compare it to the surge wattage of your devices.
Don't forget efficiency. Inverters aren't 100% efficient; some power is lost in the conversion process. A good inverter will have an efficiency rating of 85% or higher. Keep this in mind when calculating your power needs, and choose an inverter that's efficient enough to deliver the power you need without wasting too much energy. And last of all, remember to check if the inverter is UL listed.
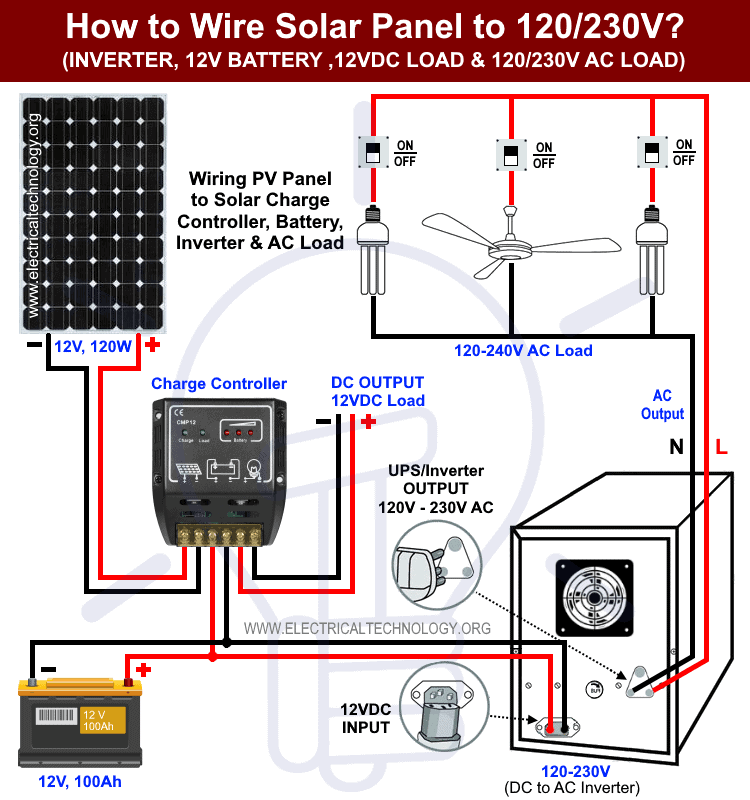
Troubleshooting Common Issues
5. Addressing Connection Problems and Battery Drain
Even with careful planning, things can sometimes go wrong. Maybe your inverter isn't working as expected, or your batteries are draining faster than they should. Don't panic! Most of these issues can be resolved with a bit of troubleshooting. Some batteries might be defected, so it is worth checking the voltage with a multimeter individually.
Check your connections. Make sure all your connections are tight and clean. Loose or corroded connections can cause voltage drops and reduce the efficiency of your system. Clean any corroded terminals with a wire brush and apply a thin coat of dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
Test your batteries. Use a multimeter to check the voltage of each battery. If one battery is significantly lower than the others, it may be defective and need to be replaced. Also, consider getting your batteries load-tested to see how they perform under a load. Most auto parts stores offer free battery load testing.
Look for parasitic loads. Even when your devices are turned off, some may still draw power from your batteries. These are called parasitic loads. To minimize parasitic loads, unplug any devices that aren't being used, or install a battery disconnect switch to completely disconnect your batteries from the system when it's not in use.
Monitor your system. Keep an eye on your battery voltage and inverter output. If you notice any unusual behavior, investigate the cause and take corrective action. There are many battery monitors available that will allow you to closely monitor the voltage and current of your system. Early detection of problems can prevent more serious damage down the road.
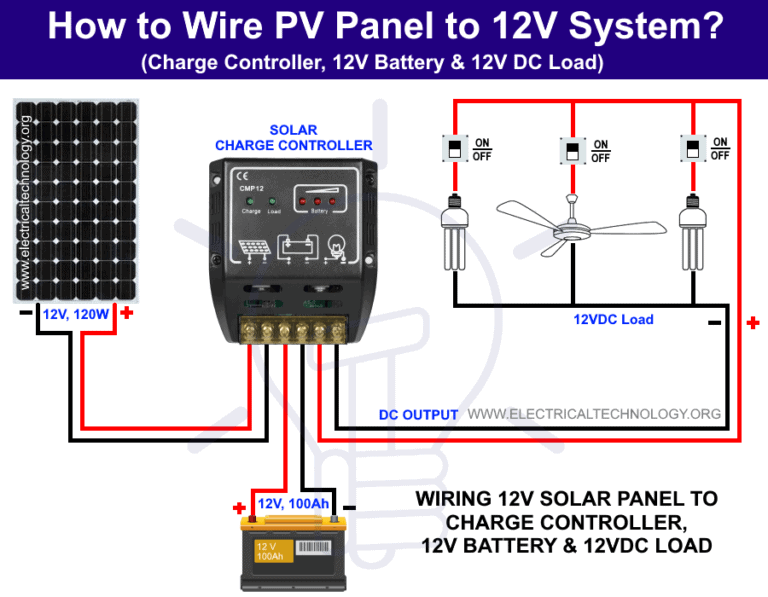
12v Inverter Battery Wiring Diagram
FAQ
6. Quick Solutions to Common Concerns
Got more questions? You're not alone! Here are some frequently asked questions about connecting batteries to inverters:
Q: Can I use different types of 12V batteries together (e.g., lead-acid and AGM)?A: It's generally not recommended. Different battery types have different charging requirements, and mixing them can lead to uneven charging and reduced lifespan for all the batteries. Stick to using the same type, age and model of battery for optimal performance.
Q: How do I know what size inverter I need?A: Add up the wattage of all the devices you plan to run simultaneously. Then, choose an inverter that has a continuous wattage rating that's at least 20% higher than that total to accommodate surge loads. And be sure to account for the inverter's efficiency rating.
Q: What happens if I connect the batteries incorrectly?A: Connecting batteries incorrectly can cause a short circuit, which can damage your batteries, your inverter, and even cause a fire. Always double-check your wiring before connecting anything. If you're unsure, consult a professional.